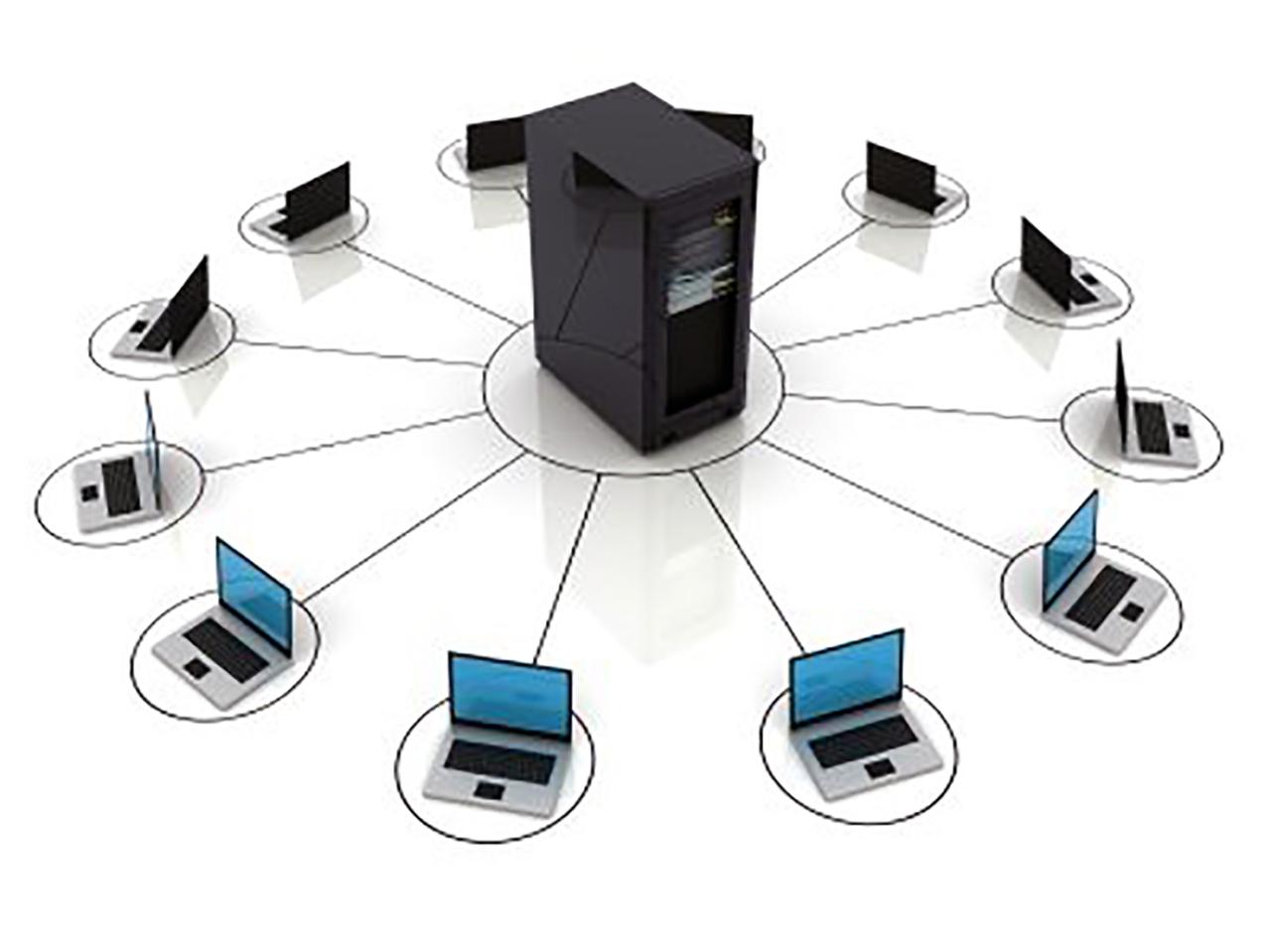
Print servers are the unsung heroes of network printing, quietly managing and facilitating the seamless flow of documents from computers to printers. They act as a central hub, simplifying printer management, enhancing security, and providing a cost-effective solution for sharing printers across a network.
Imagine a world where every computer needs a dedicated printer connection. This is where print servers come in, eliminating the need for individual printer connections and streamlining the printing process for all users on a network. They enable users to easily access and print to shared printers, regardless of their physical location, making it convenient and efficient for businesses and individuals alike.
What is a Print Server?
A print server acts as a central hub that manages and facilitates printing tasks within a network. It allows multiple computers to share a single printer, simplifying the printing process and eliminating the need for individual printer connections to each device.
Key Functionalities and Features of a Print Server
Print servers offer various functionalities that enhance printing efficiency and management:
- Print Queue Management: Print servers manage print jobs from multiple users, prioritizing and scheduling tasks based on urgency and print settings.
- Remote Printing: Users can print from any location on the network, regardless of their physical proximity to the printer.
- Access Control: Print servers enable administrators to set access permissions for different users and groups, controlling who can print and what documents they can print.
- Printer Sharing: Multiple computers can share a single printer, reducing costs and space requirements.
- Security Features: Print servers often include security features such as password protection and encryption, ensuring data confidentiality during transmission.
- Monitoring and Reporting: Print servers provide tools for monitoring print activity, tracking usage, and generating reports on printer performance.
- Print Driver Management: Print servers simplify the management of printer drivers, ensuring compatibility across different operating systems and devices.
Comparison with Traditional Printer Setup
A traditional printer setup involves connecting each computer directly to a printer using a USB cable or parallel port. This method can be cumbersome, especially in a multi-user environment, as it requires individual printer installations and driver management for each computer. In contrast, a print server centralizes printing tasks, simplifying management and eliminating the need for individual connections.
Types of Print Servers
Print servers are available in various forms:
- Hardware Print Servers: These are dedicated physical devices that act as standalone print servers. They typically offer advanced features and robust performance, making them suitable for larger networks and high-volume printing environments.
- Software Print Servers: Software-based print servers are installed on a computer within the network, acting as a virtual print server. They are often more affordable than hardware solutions and are suitable for smaller networks.
- Cloud-Based Print Servers: Cloud-based print servers leverage cloud computing infrastructure to manage printing tasks. They offer scalability, accessibility from any location, and reduced infrastructure costs, making them suitable for organizations with remote workers or geographically dispersed teams.
Print Server Architecture
A print server acts as a central hub for managing and facilitating printing tasks within a network. It simplifies the process of sharing printers among multiple computers, allowing users to access and print documents from various devices without needing to connect directly to the printer.
Print Server Architecture
The architecture of a print server typically involves a dedicated computer or a software solution installed on a network server. It acts as an intermediary between client computers and the printer, managing print jobs and ensuring smooth data transfer.
Role of the Print Server in a Network
The print server plays a crucial role in a network by:
- Centralized Print Management: The print server provides a single point of administration for managing all printers connected to the network. This includes tasks like adding and removing printers, configuring print settings, and monitoring printer status.
- Print Job Routing and Queuing: The print server receives print jobs from client computers and manages the order in which they are sent to the printer. It acts as a buffer, holding print jobs in a queue until the printer is ready to receive them.
- Print Spooling: The print server spools print jobs, meaning it temporarily stores the print data in its memory or on its hard drive. This allows client computers to continue working without waiting for the printer to finish printing.
- Security and Access Control: The print server can be configured to restrict access to specific printers or enforce printing policies, ensuring only authorized users can print documents.
Components of a Print Server System
A print server system typically consists of the following components:
- Print Server Hardware: This can be a dedicated computer or a server with specific hardware configurations to handle print jobs efficiently.
- Print Server Software: The print server software is responsible for managing print jobs, configuring printers, and providing a user interface for administration.
- Network Interface Card (NIC): The print server needs a network interface card to connect to the network and communicate with client computers and printers.
- Printers: The print server connects to one or more printers, allowing users to print documents from various devices.
Data Flow in a Print Server System
The data flow in a print server system follows these steps:
- Client Computer Sends Print Job: A client computer sends a print job to the print server, including the document to be printed and any associated print settings.
- Print Server Receives and Processes Print Job: The print server receives the print job and processes it, converting the document to a printer-specific format.
- Print Server Sends Print Job to Printer: The print server sends the print job to the selected printer, which receives and prints the document.
- Print Server Notifies Client Computer: Once the print job is complete, the print server notifies the client computer, indicating that the printing process is finished.
Print Server Protocols and Standards

Print servers rely on specific protocols and standards to facilitate communication between devices and manage printing operations. These protocols define the rules and formats for data exchange, ensuring smooth and efficient printing.
Print Server Protocols
Print server protocols dictate the way devices communicate with each other during printing. Common protocols include:
- Line Printer Daemon (LPD): A long-standing protocol, LPD uses a simple text-based format for sending print jobs. It is primarily used for traditional Unix and Linux systems.
- Server Message Block (SMB): Primarily used for file sharing, SMB can also handle print jobs. It is widely supported by Windows and other operating systems, offering a robust and secure printing solution.
- Internet Printing Protocol (IPP): A modern and standardized protocol designed specifically for network printing. IPP uses XML-based messages for communication, enabling advanced features like print queue management, job status tracking, and printer configuration.
Comparison of Print Server Protocols
Print server protocols vary in their features, security, and performance. A comparison of LPD, SMB, and IPP highlights their strengths and weaknesses:
| Protocol | Strengths | Weaknesses |
|---|---|---|
| LPD | Simple and lightweight; widely supported. | Limited features; less secure than newer protocols. |
| SMB | Robust and secure; widely supported. | Not specifically designed for printing; can be complex to configure. |
| IPP | Modern and standardized; offers advanced features. | Requires more resources; may not be supported by older printers. |
Significance of Industry Standards
Industry standards like IPP play a crucial role in ensuring interoperability and seamless printing. They provide a common framework for print server communication, allowing devices from different manufacturers to interact smoothly. This standardization facilitates:
- Device Compatibility: Printers and computers from different manufacturers can seamlessly communicate and print documents.
- Simplified Management: Administrators can manage print queues and printer settings centrally, regardless of the specific device model.
- Enhanced Security: Standards like IPP incorporate security measures to protect print jobs and prevent unauthorized access.
Setting Up and Configuring a Print Server
Setting up and configuring a print server involves several steps, including installing the necessary software, adding printers to the server, and configuring essential settings for optimal performance. The process can vary slightly depending on the print server software you choose and the operating system of your server.
Installing and Configuring Print Server Software
Print server software provides the interface and functionality needed to manage printers and share them with other devices on the network.
- Download and Install the Software: Choose a print server software that meets your needs and is compatible with your operating system. Download the software from the vendor’s website and follow the installation instructions.
- Configure the Software: After installation, you’ll need to configure the print server software. This typically involves specifying the network settings, such as the IP address and subnet mask, and defining user access permissions.
- Set Up Security: Configure security settings to protect the print server from unauthorized access. This might involve setting up passwords, enabling firewalls, and configuring user authentication.
Adding Printers to the Print Server
Once the print server software is installed and configured, you can add printers to the server.
- Connect Printers: Connect the printers to the print server either directly via USB or network cable or wirelessly.
- Add Printers in the Software: Use the print server software to add the printers. This usually involves selecting the printer model, specifying the connection type, and providing a printer name.
- Configure Printer Settings: After adding the printer, you may need to configure additional settings, such as paper size, orientation, and default print quality.
Configuring Essential Settings for Print Server Performance
Optimizing print server performance involves configuring settings to ensure smooth printing and efficient resource utilization.
- Spooler Settings: The print spooler manages print jobs. You can adjust spooler settings to optimize the print queue, such as setting the maximum number of print jobs in the queue and the priority of jobs.
- Printer Driver Settings: Printer drivers control how the print server interacts with the printers. Ensure you are using the latest drivers and adjust driver settings to optimize print quality and speed.
- Network Settings: Network settings play a crucial role in print server performance. Configure the network settings to ensure optimal bandwidth allocation and minimize network latency.
Print Server Management
Managing a print server effectively is crucial for maintaining a smooth and efficient printing environment. A well-managed print server ensures that users can access printers easily, print jobs are processed promptly, and potential issues are addressed proactively.
Monitoring Print Server Activity
Monitoring print server activity is essential for identifying potential problems, optimizing performance, and ensuring security. This involves tracking key metrics like print job volume, print queue sizes, printer status, and network traffic related to printing.
- Print Server Logs: Print servers generate logs that record various events, including print job submissions, print queue activity, printer errors, and security events. Regularly reviewing these logs can help identify patterns, troubleshoot issues, and detect potential security threats.
- Network Monitoring Tools: Network monitoring tools can be used to track network traffic related to printing, identifying potential bottlenecks or unusual activity that might indicate a print server issue.
- Print Server Management Consoles: Many print servers come with dedicated management consoles that provide a centralized interface for monitoring print queues, printer status, and other relevant information.
- Third-Party Monitoring Tools: Specialized third-party monitoring tools can offer more comprehensive print server monitoring capabilities, including performance analysis, alerts, and reporting.
Troubleshooting Common Print Server Issues
Print server issues can range from simple connectivity problems to complex software conflicts. A systematic approach to troubleshooting can help isolate and resolve these issues efficiently.
- Connectivity Problems: Verify network connectivity between the print server, client computers, and printers. Check cable connections, network settings, and firewall rules.
- Print Queue Issues: Examine the print queue for any stuck or stalled jobs. Delete any problematic jobs and restart the print spooler service.
- Driver Conflicts: Ensure that the correct printer drivers are installed on both the print server and client computers. Update drivers if necessary.
- Permissions and Access Control: Verify that users have appropriate permissions to access the print server and printers.
- Printer Hardware Issues: Check the physical connection of the printer, its power supply, and the paper tray. If necessary, run printer diagnostics or contact the printer manufacturer for support.
Maintaining Print Server Security
Protecting the print server from unauthorized access and security threats is crucial. Implementing robust security measures helps prevent data breaches and ensures the integrity of the printing environment.
- Strong Passwords and Access Control: Enforce strong passwords for all users and administrators who have access to the print server. Implement granular access control policies to restrict access to specific printers or print queues based on user roles.
- Regular Security Updates: Keep the print server operating system, print server software, and printer drivers up to date with the latest security patches and updates.
- Firewall Protection: Configure a firewall on the print server to block unauthorized access and protect against malicious network traffic.
- Antivirus Software: Install and maintain up-to-date antivirus software on the print server to detect and remove malware.
- Secure Print Protocols: Use secure print protocols like HTTPS and IPsec to encrypt communication between the print server, client computers, and printers.
Print Server Security
Print servers, like any other network device, are susceptible to various security threats that can compromise data confidentiality, integrity, and availability. Implementing robust security measures is crucial to protect sensitive information and ensure smooth print operations.
Potential Security Threats, Print server
Print servers face several potential security threats, including:
- Unauthorized Access: Malicious actors may attempt to gain unauthorized access to the print server, potentially exploiting vulnerabilities or weak passwords. This could allow them to steal data, modify print jobs, or disrupt print services.
- Malware Infections: Print servers can be infected with malware, such as viruses or ransomware, through various means, including email attachments, infected files, or network vulnerabilities. Infected print servers can spread malware to other devices on the network or be used as a launchpad for further attacks.
- Data Breaches: Print server data, including print job history, user credentials, and printer configurations, can be targeted by attackers. Data breaches can expose sensitive information and compromise user privacy.
- Denial of Service (DoS) Attacks: Attackers can launch DoS attacks to overwhelm the print server with excessive traffic, rendering it unavailable for legitimate users. This can disrupt print operations and impact productivity.
Security Measures
To mitigate security risks and protect print server data, organizations should implement a comprehensive security strategy that includes:
- Strong Passwords and Access Control: Implementing strong passwords and access control measures is fundamental to securing print servers. Enforce password complexity requirements, such as using a combination of uppercase and lowercase letters, numbers, and special characters, and encourage regular password changes. Limit user access to the print server based on their roles and responsibilities, granting only necessary permissions.
- Firewall Protection: Deploy a firewall to filter incoming and outgoing network traffic, blocking unauthorized access to the print server. Configure the firewall to allow only necessary traffic and block suspicious connections. Regularly update firewall rules and ensure they are effectively protecting the print server.
- Regular Security Updates: Keep the print server operating system, firmware, and software applications up to date. Software updates often include security patches that address vulnerabilities and mitigate risks. Enable automatic updates to ensure timely security patches are applied.
- Network Segmentation: Isolate the print server from other sensitive network segments, such as the corporate network or the internet. This reduces the attack surface and prevents malware from spreading to other systems. Network segmentation helps contain security breaches and minimizes the impact of potential attacks.
- Anti-Malware Software: Install and maintain anti-malware software on the print server to detect and remove malicious programs. Regularly update the anti-malware software to ensure it can identify and neutralize the latest threats. Consider using a multi-layered approach with different anti-malware solutions for enhanced protection.
- Data Encryption: Encrypt print data in transit and at rest to protect sensitive information from unauthorized access. Encryption ensures that even if data is intercepted, it cannot be deciphered without the appropriate decryption key. Implement encryption protocols like SSL/TLS for data transmission and use strong encryption algorithms for data storage.
- Regular Security Audits: Conduct regular security audits to identify vulnerabilities and weaknesses in the print server environment. Audits should assess security controls, network configuration, and user access permissions. Identify and address any security gaps to enhance the overall security posture.
- Security Awareness Training: Educate users about security best practices and potential threats. Train them on how to identify and avoid phishing attacks, recognize suspicious emails, and report security incidents. Encourage users to use strong passwords and practice safe browsing habits.
Access Control and Authentication
Access control and authentication are essential security measures to protect print server resources and ensure only authorized users can access and manage print jobs.
- Role-Based Access Control (RBAC): Implement RBAC to define user roles and assign specific permissions based on their job functions. This ensures users have access only to the resources they need and prevents unauthorized access to sensitive information.
- Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA): Implement MFA to enhance user authentication by requiring users to provide multiple forms of identification, such as a password and a one-time code from a mobile device. MFA adds an extra layer of security, making it more difficult for unauthorized individuals to gain access to the print server.
- Secure Authentication Protocols: Use secure authentication protocols like Kerberos or LDAP to authenticate users and grant access to the print server. These protocols provide strong authentication and authorization mechanisms, ensuring that only legitimate users can access the print server.
Best Practices for Securing a Print Server Environment
Implementing best practices is crucial to maintain a secure print server environment:
- Regularly Review Security Policies: Regularly review and update security policies to reflect evolving threats and industry best practices. Ensure policies address password complexity, access control, security updates, and incident response procedures.
- Implement Strong Password Policies: Enforce strong password policies for all users accessing the print server. Require users to use a combination of uppercase and lowercase letters, numbers, and special characters. Encourage regular password changes to prevent unauthorized access.
- Restrict User Access: Grant only necessary permissions to users accessing the print server. Implement the principle of least privilege, ensuring users have access only to the resources they need to perform their job functions.
- Monitor Print Server Activity: Monitor print server activity for suspicious patterns or anomalies. This can help identify potential security breaches and respond promptly to threats. Use security information and event management (SIEM) tools to analyze log data and detect unusual activity.
- Implement Incident Response Plan: Develop a comprehensive incident response plan to handle security breaches effectively. The plan should Artikel steps to contain the incident, mitigate damage, recover data, and restore operations. Regularly test the incident response plan to ensure its effectiveness.
Print Server for Mobile Devices

In today’s mobile-centric world, it’s essential for print servers to seamlessly integrate with smartphones and tablets. Print servers provide a convenient and efficient way to print documents and images from mobile devices, offering flexibility and accessibility to users.
Printing from Mobile Devices
Print servers enable users to print documents and images from their smartphones and tablets using various methods. These methods often involve using mobile printing apps that connect to the print server, allowing users to select the desired printer and print their documents wirelessly.
Mobile Printing Apps and Solutions
Several mobile printing apps and solutions are available, each offering different features and functionalities. Some popular options include:
- Google Cloud Print: A cloud-based printing service that allows users to print from any device to any printer connected to the internet. It offers a convenient and platform-independent printing solution.
- HP ePrint: HP’s cloud printing service enables users to print from any device to any HP printer connected to the internet. It offers features like email-based printing and mobile printing apps.
- Canon PRINT Inkjet/SELPHY: Canon’s mobile printing app allows users to print photos, documents, and web pages from their smartphones and tablets to Canon printers.
- Brother iPrint&Scan: Brother’s mobile printing app allows users to print documents, photos, and web pages from their smartphones and tablets to Brother printers.
- Epson iPrint: Epson’s mobile printing app allows users to print documents, photos, and web pages from their smartphones and tablets to Epson printers.
Advantages of Mobile Printing with a Print Server
Mobile printing with a print server offers numerous advantages, including:
- Convenience and Accessibility: Users can print from anywhere with an internet connection, eliminating the need to be physically near a printer.
- Flexibility and Portability: Mobile printing allows users to print documents and images from their smartphones and tablets, providing greater flexibility and portability.
- Cost Savings: Mobile printing can reduce printing costs by eliminating the need for dedicated desktop printers for each user.
- Enhanced Productivity: Mobile printing allows users to print documents and images quickly and efficiently, enhancing productivity and streamlining workflows.
- Improved Security: Print servers can be configured with security measures to protect sensitive data and prevent unauthorized access.
Print Server in the Cloud
A cloud-based print server, also known as a cloud print service, offers a virtualized print server solution hosted on a remote server infrastructure accessible via the internet. This approach eliminates the need for a dedicated physical print server on your local network. Instead, users connect to the cloud print service to manage and access printers.
Benefits of Cloud Print Servers
Cloud print servers offer numerous advantages over traditional on-premises solutions. Here are some key benefits:
- Cost-Effectiveness: Cloud print servers eliminate the need for upfront hardware purchases and ongoing maintenance costs associated with physical print servers. The pay-as-you-go pricing model of cloud services makes them budget-friendly, especially for small and medium-sized businesses.
- Scalability and Flexibility: Cloud print servers can easily scale up or down to accommodate changes in printing demands. As your business grows or shrinks, you can adjust your cloud print service plan to match your needs.
- Accessibility and Mobility: Cloud print servers provide users with remote access to printers from anywhere with an internet connection. This is particularly beneficial for mobile workforces and remote employees.
- Centralized Management: Cloud print servers offer a centralized platform for managing all your printers and users. This simplifies administration tasks, such as adding new printers, configuring settings, and monitoring print usage.
- Enhanced Security: Cloud print servers often benefit from robust security measures implemented by the cloud provider. These measures can include data encryption, access control, and regular security updates, providing a more secure printing environment compared to traditional on-premises servers.
- Automatic Updates: Cloud print servers are automatically updated with the latest security patches and software updates, eliminating the need for manual intervention. This ensures that your print infrastructure remains secure and up-to-date.
Comparison with Traditional Print Servers
| Feature | Cloud Print Server | Traditional Print Server |
|---|---|---|
| Deployment | Hosted on a remote server infrastructure | Installed on a physical server on your local network |
| Cost | Pay-as-you-go subscription model | Upfront hardware purchase and ongoing maintenance costs |
| Scalability | Easily scalable to meet changing printing needs | Requires physical hardware upgrades to accommodate growth |
| Accessibility | Remote access from anywhere with an internet connection | Limited to devices on the local network |
| Management | Centralized management platform | Requires on-site administration and configuration |
| Security | Robust security measures implemented by the cloud provider | Relies on local security measures and updates |
| Updates | Automatic updates provided by the cloud provider | Manual updates required for security patches and software upgrades |
Examples of Cloud Print Server Services
Here are some examples of popular cloud print server services:
- Google Cloud Print: Google Cloud Print is a service that allows users to print from any device with an internet connection to any printer that supports Google Cloud Print. It is a popular choice for individuals and small businesses.
- PrinterLogic: PrinterLogic is a cloud-based print management solution that provides a centralized platform for managing all your printers and users. It offers features such as secure print release, mobile printing, and print auditing.
- PaperCut MF: PaperCut MF is a comprehensive print management solution that includes a cloud-based print server. It offers features such as print quotas, cost recovery, and secure print release.
Future Trends in Print Server Technology
The landscape of print server technology is continuously evolving, driven by the increasing adoption of cloud computing, mobile devices, and the growing demand for secure and efficient printing solutions. These advancements are shaping the future of print server technology, leading to more innovative and user-friendly solutions.
Impact of Cloud Computing and Mobile Devices
The rise of cloud computing and mobile devices has significantly impacted print server technology. Cloud-based print services offer numerous advantages, such as scalability, cost-effectiveness, and remote accessibility. Mobile printing solutions allow users to print documents from anywhere using their smartphones or tablets.
- Cloud-Based Print Services: Cloud-based print services enable organizations to access and manage their printers remotely, eliminating the need for on-premises print servers. This offers benefits like scalability, cost-effectiveness, and reduced IT overhead. Examples of cloud-based print services include Google Cloud Print, HP Instant Ink, and Microsoft Azure Print.
- Mobile Printing: Mobile printing solutions have become increasingly popular, allowing users to print documents from their smartphones or tablets. These solutions leverage cloud services and wireless connectivity to enable seamless printing from anywhere. Examples include Mopria, Apple AirPrint, and Google Cloud Print.
Future Developments and Innovations
The future of print server technology is characterized by ongoing innovation, with a focus on enhanced security, improved user experience, and integration with emerging technologies.
- Advanced Security Features: Print server technology is incorporating advanced security features to protect sensitive data and prevent unauthorized access. These features include encryption, authentication, and access control mechanisms.
- Artificial Intelligence (AI) Integration: AI is being integrated into print servers to optimize print jobs, manage print queues, and provide predictive maintenance. AI algorithms can analyze printing patterns and identify potential issues, improving efficiency and reducing downtime.
- Internet of Things (IoT) Integration: Print servers are increasingly being integrated with IoT devices, enabling remote monitoring, management, and troubleshooting. This allows IT administrators to remotely track printer status, manage consumables, and receive alerts in case of any issues.
- Sustainable Printing: Print server technology is evolving to support sustainable printing practices. Features like automatic duplex printing, paperless workflows, and toner recycling are being incorporated to reduce environmental impact.
Evolution of Print Server Technology
Print server technology will continue to evolve to meet the changing needs of businesses and individuals. The focus will be on simplifying print management, improving security, and enhancing user experience.
- Simplified Print Management: Print server technology is becoming more user-friendly, with intuitive interfaces and automated tasks. This simplifies print management for both IT administrators and end users.
- Enhanced Security: Security remains a top priority, with print servers incorporating advanced encryption, authentication, and access control mechanisms to protect sensitive data.
- Improved User Experience: Print server technology is designed to provide a seamless and efficient printing experience. Features like mobile printing, cloud integration, and automated workflows enhance user convenience.
Conclusion
Print servers are essential components of modern networks, offering a robust and reliable solution for managing and controlling printing operations. From simplifying printer management to enhancing security and cost-effectiveness, print servers play a crucial role in ensuring seamless and efficient printing across a network. As technology continues to evolve, print servers are adapting to meet new demands, integrating with mobile devices and leveraging cloud-based solutions to provide even greater flexibility and accessibility. In the future, print servers will continue to be a vital part of network infrastructure, supporting the needs of businesses and individuals alike.
Print servers are essential for managing and sharing printers across a network, but choosing the right hardware can be tricky. If you’re looking for a powerful and reliable platform, consider the HP DL380 Gen10 server. You can find detailed specifications and features on the dl380 gen10 quickspecs page, which will help you determine if it’s the right fit for your print server needs.
With its robust performance and scalability, the DL380 Gen10 can handle even the most demanding print workloads.