Bluehost nameservers are the backbone of your website’s online presence, acting as the bridge between your domain name and your website’s files hosted on Bluehost’s servers. Understanding how nameservers work is crucial for managing your domain, ensuring your website loads correctly, and even enhancing its security and performance.
This guide explores the intricacies of Bluehost nameservers, covering topics like default settings, customization options, troubleshooting tips, and best practices for managing them effectively. We’ll delve into the relationship between domain names, DNS, and nameservers, and discuss the impact of nameserver settings on your website’s speed, reliability, and security. Whether you’re a seasoned website owner or a curious newcomer, this comprehensive guide will equip you with the knowledge you need to navigate the world of Bluehost nameservers with confidence.
Introduction to Bluehost Nameservers
Bluehost nameservers play a crucial role in connecting your domain name to your website’s physical location on the internet. They act as the bridge between your website’s address (domain name) and its actual server location, ensuring that visitors can access your website correctly.
Domain Names, DNS, and Nameservers, Bluehost nameservers
Domain names, DNS, and nameservers work together to make the internet accessible and user-friendly. When you type a website address into your browser, your computer first contacts a DNS server. This server translates the human-readable domain name into a numerical IP address, which is the website’s actual location on the internet. Nameservers are responsible for storing and managing this information.
Bluehost’s Hosting Services
Bluehost is a well-known web hosting provider that offers a range of services, including shared hosting, VPS hosting, dedicated hosting, and WordPress hosting. These services provide the necessary infrastructure for websites to operate online. Bluehost’s nameservers are an integral part of its hosting services, ensuring that your website is accessible and reliable.
Default Nameservers for Bluehost

Bluehost automatically assigns default nameservers to your domain when you sign up for their hosting services. These nameservers are responsible for connecting your domain name to your website’s files stored on Bluehost’s servers.
The default nameservers are designed to work seamlessly with Bluehost’s infrastructure, ensuring that your website loads quickly and reliably.
Advantages and Disadvantages of Using Default Nameservers
Using default nameservers offers convenience and simplicity. However, there are also some potential drawbacks to consider.
Advantages
- Easy Setup: Bluehost automatically configures the default nameservers for your domain, eliminating the need for manual configuration. This simplifies the setup process for new users.
- Optimized for Bluehost: Default nameservers are specifically designed to work with Bluehost’s hosting infrastructure, ensuring optimal performance and reliability for your website.
- No Need for Advanced Knowledge: You don’t need any technical expertise to use default nameservers. Bluehost handles the technical aspects, making it suitable for beginners.
Disadvantages
- Limited Customization: You cannot customize the default nameservers. This limits your ability to fine-tune DNS settings for specific needs, such as improving website security or performance.
- Potential Performance Issues: If you experience performance issues with your website, the default nameservers might be a contributing factor. The default nameservers might not be the most efficient for all website configurations.
- Limited Control: Using default nameservers means you have less control over your domain’s DNS settings. This can be a concern if you require advanced DNS management for specific applications.
When to Change Default Nameservers
There are specific situations where you might need to change the default nameservers assigned by Bluehost.
- Transferring Your Domain: If you’re moving your domain to a different hosting provider, you’ll need to update the nameservers to point to the new host’s servers.
- Using a Custom DNS Service: Some users prefer to use a third-party DNS service for advanced features or better performance. In such cases, you’ll need to change the nameservers to the ones provided by the DNS service.
- Improving Website Security: If you want to enhance your website’s security, you might consider using a DNS service that offers security features like DNSSEC. This requires changing the nameservers to the ones provided by the security service.
- Optimizing Website Performance: If you’re experiencing slow website loading times, changing the nameservers to a faster DNS service can potentially improve performance.
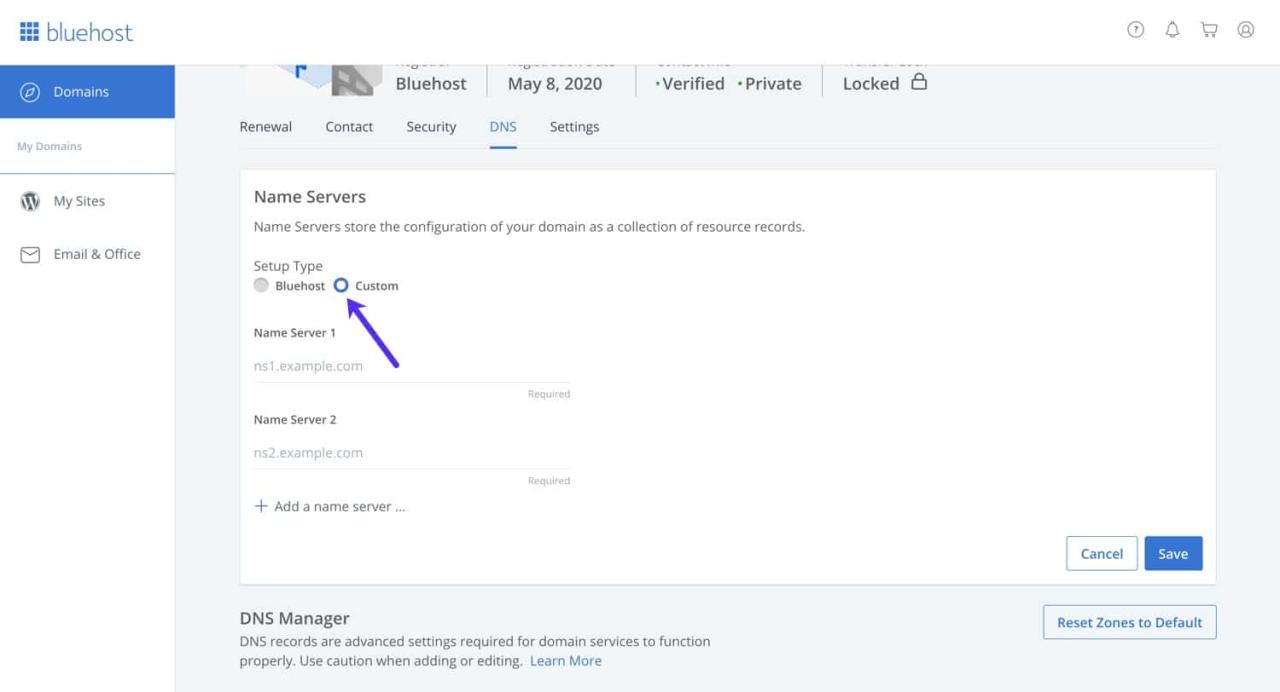
Customizing Nameserver Settings
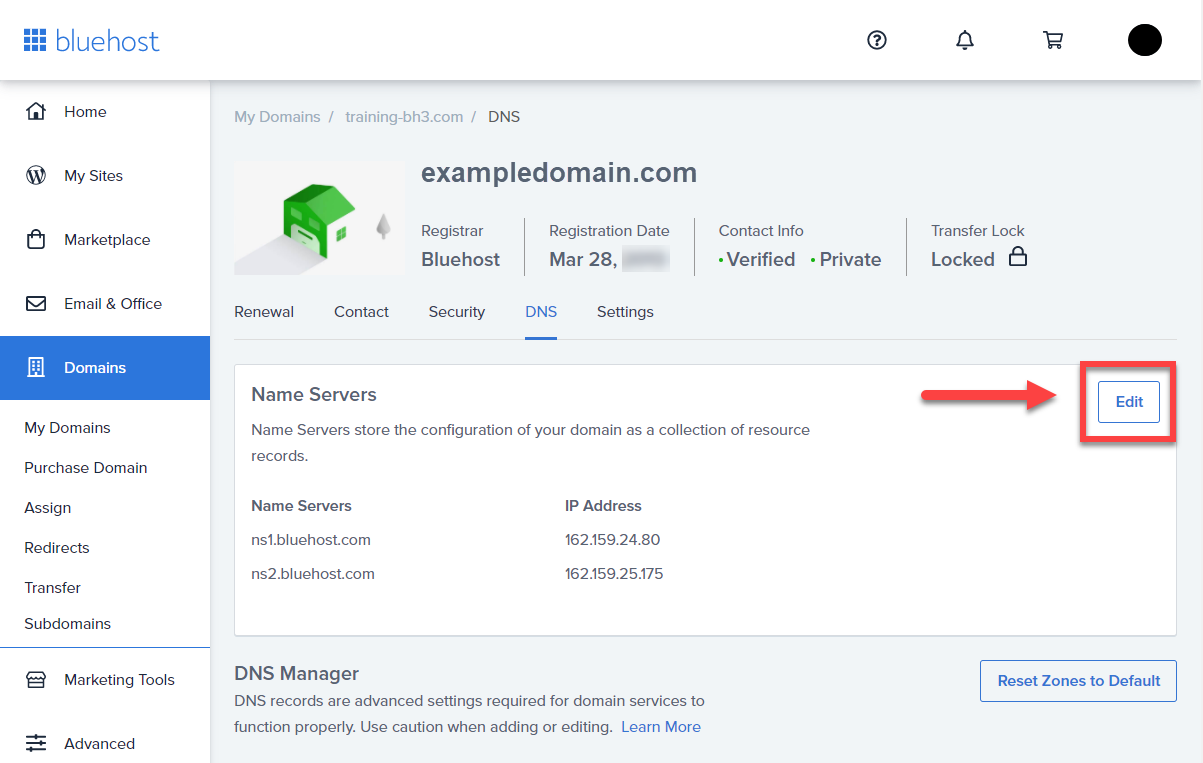
Changing nameserver settings for your domain hosted with Bluehost is a powerful tool that allows you to control how your domain is routed and managed. This process involves updating the nameserver records associated with your domain to point to different servers.
Potential Implications of Changing Nameserver Settings
Modifying nameserver settings can have a significant impact on your website’s functionality and accessibility. It’s crucial to understand the potential implications before making any changes.
- Website Downtime: Changing nameservers can temporarily interrupt website access as the DNS system updates. This downtime can last anywhere from a few minutes to a few hours, depending on the propagation time for the changes.
- Email Service Disruption: If your email service is hosted on the same servers as your website, changing nameservers could disrupt email functionality. This is because email relies on DNS records to route messages correctly.
- Security Risks: If you choose to use third-party nameservers, there’s a potential security risk if the provider is not reputable. Ensure that the nameservers you select are reliable and secure to avoid compromising your domain and website.
Choosing Appropriate Nameservers for Specific Needs
The appropriate nameservers for your domain depend on your specific needs and preferences.
- Bluehost Nameservers: If you’re using Bluehost for web hosting, using their default nameservers is generally recommended. This ensures seamless integration with your hosting environment and simplifies domain management.
- Third-Party Nameservers: Some users might prefer to use third-party nameservers for reasons like increased security, improved performance, or advanced DNS features. Popular options include Cloudflare, Google Domains, and Amazon Route 53. When choosing third-party nameservers, ensure they are reputable and provide the features you need.
- Custom Nameservers: If you have a specific technical need or require granular control over your DNS settings, you might consider setting up your own custom nameservers. This approach requires advanced technical knowledge and expertise.
Troubleshooting Nameserver Issues
Nameservers play a crucial role in directing website traffic to the correct server. When nameservers are misconfigured or encounter issues, it can lead to website downtime, slow loading speeds, or even inaccessibility. This section will explore common nameserver problems and guide you through troubleshooting steps to resolve them.
Identifying Common Nameserver Issues
Nameserver issues can manifest in various ways, impacting your website’s performance and availability. Understanding these common problems is crucial for effective troubleshooting.
- Incorrect Nameserver Configuration: Misconfigured nameservers are a frequent cause of website problems. Double-checking your nameserver settings and ensuring they are accurate is essential.
- DNS Propagation Delays: After updating nameservers, it takes time for the changes to propagate across the global DNS network. This delay can cause temporary website inaccessibility or inconsistent behavior.
- Nameserver Downtime: Nameserver outages can occur due to technical issues or server failures. This can result in complete website inaccessibility until the nameservers are restored.
- Caching Issues: DNS caching can sometimes cause outdated information to be served, even after nameserver changes. Clearing browser cache and DNS cache can help resolve this issue.
Troubleshooting Steps for Nameserver Issues
When encountering nameserver problems, a systematic approach to troubleshooting is essential. Here’s a step-by-step guide to help you identify and resolve common issues:
- Verify Nameserver Settings: The first step is to confirm that your nameservers are correctly configured. Check your domain registrar’s control panel or Bluehost’s dashboard for the correct nameserver settings. Ensure they match the intended nameservers for your website.
- Check DNS Propagation: After updating nameservers, it’s crucial to allow sufficient time for DNS propagation. This process can take up to 48 hours to complete. Use a DNS checker tool to monitor propagation progress and confirm that the changes have been implemented across the DNS network.
- Clear DNS Cache: DNS caching can sometimes cause outdated information to be served. Clearing your browser cache and DNS cache can help ensure that you are accessing the latest information. You can find instructions for clearing cache on various operating systems and browsers online.
- Contact Bluehost Support: If you are unable to resolve the issue independently, contacting Bluehost support is the best course of action. They can assist you with advanced troubleshooting steps and provide tailored solutions to your specific problem.
Additional Resources for Nameserver Troubleshooting
Besides the steps Artikeld above, several resources can help you further understand and troubleshoot nameserver issues.
- Bluehost Knowledge Base: Bluehost provides extensive documentation and troubleshooting guides in their knowledge base. You can find articles on various topics, including nameservers, DNS configuration, and common website problems.
- Online DNS Checker Tools: Various online tools can help you check DNS propagation, identify nameserver issues, and monitor your website’s DNS records. These tools provide valuable insights into your website’s DNS configuration and can assist in resolving problems.
- Community Forums: Online forums dedicated to web hosting and DNS management can be valuable resources for seeking advice and sharing experiences with other users. Engaging with the community can provide alternative solutions and perspectives on common nameserver issues.
Impact of Nameservers on Website Performance
Nameservers play a crucial role in website performance, influencing how quickly visitors can access your website and how reliably it operates. Understanding how nameserver settings affect these aspects is essential for optimizing your website’s overall user experience.
DNS Caching and Website Performance
DNS caching is a vital mechanism that significantly impacts website performance. When a user tries to access a website, their browser first contacts a DNS resolver to translate the website’s domain name into its corresponding IP address. This process involves querying various DNS servers across the internet. To speed up this process, DNS resolvers store recently resolved domain names and their IP addresses in a local cache. This means that subsequent requests for the same website can be served directly from the cache, eliminating the need for repeated DNS lookups.
Optimizing Nameserver Settings for Improved Performance
Several strategies can be employed to optimize nameserver settings for improved website performance:
- Choose Reliable Nameservers: Selecting robust and dependable nameservers is paramount. Reliable nameservers minimize downtime and ensure consistent DNS resolution. Consider using nameservers from reputable hosting providers or CDNs, which often offer high availability and redundancy.
- Minimize Time-to-Live (TTL) Values: The TTL value specifies how long DNS records are cached by resolvers. Lower TTL values, such as 300 seconds or less, allow for faster updates to DNS records, which can be beneficial when making changes to your website, such as updating IP addresses or adding new domains.
- Use DNS Load Balancing: DNS load balancing distributes website traffic across multiple servers, ensuring that no single server becomes overloaded. This technique improves website responsiveness and prevents performance degradation during peak traffic periods.
- Implement DNS Anycast: DNS anycast is a technology that directs requests to the geographically closest server, minimizing latency and improving website performance for users worldwide. This approach is particularly beneficial for websites with a global audience.
Nameservers and Website Security: Bluehost Nameservers
Nameservers play a crucial role in website security by directing users to the correct server hosting your website. While they primarily focus on website accessibility, they can also impact your website’s security posture. Understanding the potential security implications of using different nameservers and implementing appropriate security measures for your nameserver settings is crucial for protecting your website from various threats.
Security Implications of Using Different Nameservers
Choosing the right nameserver provider can significantly impact your website’s security. Here’s why:
- Reliability and Uptime: A reliable nameserver provider ensures consistent and uninterrupted service, reducing the risk of downtime, which can be exploited by attackers.
- Security Measures: Nameserver providers often implement various security measures, such as DDoS protection, access control, and encryption, to protect their infrastructure and the data they manage.
- Reputation and Trust: A reputable nameserver provider with a history of strong security practices can contribute to the overall trust and security of your website.
How Nameserver Settings Contribute to Website Security
Properly configuring your nameserver settings can enhance your website’s security in several ways:
- DNSSEC: DNSSEC (Domain Name System Security Extensions) helps authenticate DNS records and prevent DNS spoofing attacks, where attackers redirect users to malicious websites.
- Access Control: Restricting access to your nameserver settings and using strong passwords can prevent unauthorized modifications that could compromise your website.
- Two-Factor Authentication: Implementing two-factor authentication for accessing your nameserver account adds an extra layer of security and makes it more difficult for attackers to gain unauthorized access.
Protecting Nameserver Settings from Unauthorized Access
To safeguard your nameserver settings from unauthorized access, consider these tips:
- Use Strong Passwords: Create complex passwords for your nameserver account and avoid using the same password for multiple accounts.
- Enable Two-Factor Authentication: Two-factor authentication adds an extra layer of security by requiring a second verification step, such as a code sent to your phone or email.
- Monitor Access Logs: Regularly review your nameserver access logs for any suspicious activity or unauthorized access attempts.
- Keep Software Up-to-Date: Regularly update your nameserver software to patch any vulnerabilities that could be exploited by attackers.
Nameservers for Subdomains
Subdomains are separate sections of your main domain, allowing you to organize content or host specific applications. Setting up nameservers for subdomains is crucial for directing traffic and ensuring they function correctly.
Understanding how nameservers work for subdomains is essential for managing your website effectively. While the process shares similarities with setting up nameservers for main domains, there are some key differences that you should be aware of. We will explore these differences and guide you through the process of configuring nameservers for subdomains hosted with Bluehost.
Configuring Nameservers for Subdomains
When you create a subdomain on Bluehost, the default nameservers will be assigned to it. However, you can customize these settings to meet your specific needs. The following steps illustrate the process of configuring nameservers for subdomains hosted with Bluehost:
- Access the Bluehost Control Panel: Log in to your Bluehost account and navigate to the Control Panel.
- Locate the Domain Manager: Find the “Domains” or “Domain Manager” section in the Control Panel.
- Select the Subdomain: Click on the subdomain you want to configure nameservers for.
- Edit Nameserver Settings: Look for the “Nameservers” or “DNS Settings” option. You will see the default nameservers assigned to the subdomain.
- Change Nameservers: Enter the desired nameservers in the provided fields. These nameservers should point to the server where your subdomain is hosted. If you’re using Bluehost, the default nameservers will likely work.
- Save Changes: Click on the “Save” or “Update” button to apply the new nameserver settings.
Examples of Subdomain Nameserver Configurations
Let’s look at some specific examples of how you can configure nameservers for subdomains based on their intended purpose:
- Blog Subdomain: If you’re hosting a blog on a subdomain like “blog.yourdomain.com,” you would configure the nameservers to point to the Bluehost server where your blog files are stored. This ensures visitors to your blog subdomain are directed to the correct location.
- Secure Subdomain: For subdomains that require secure connections (like “secure.yourdomain.com”), you’ll need to configure the nameservers to point to a server with SSL/TLS certificates installed. This ensures secure communication between visitors and your subdomain.
- External Hosting: If you’re hosting a subdomain on a different server provider, you’ll need to configure the nameservers to point to that external server. This allows visitors to access your subdomain from the correct location.
Alternatives to Bluehost Nameservers
While Bluehost provides reliable nameserver services, you might consider alternative options for specific needs or preferences. Exploring third-party nameservers can offer advantages like enhanced security, performance optimization, and cost-effectiveness.
Benefits and Drawbacks of Third-Party Nameservers
Choosing a third-party nameserver provider involves weighing benefits and drawbacks.
- Benefits:
- Enhanced Security: Third-party nameservers often implement robust security measures, such as DNSSEC (Domain Name System Security Extensions) and DDoS (Distributed Denial of Service) protection, to safeguard your domain from malicious attacks.
- Performance Optimization: Some providers offer global server networks, ensuring faster DNS resolution times and improved website loading speeds for visitors worldwide.
- Advanced Features: Third-party nameservers may provide additional features like DNS analytics, custom DNS records, and flexible configurations, catering to specific technical requirements.
- Cost-Effectiveness: Depending on your needs, third-party nameservers can offer more affordable options compared to bundled services from hosting providers.
- Drawbacks:
- Complexity: Managing nameservers independently can be more complex than relying on a hosting provider’s integrated solution, requiring technical knowledge and time commitment.
- Technical Support: While most providers offer support, it might not be as readily available or comprehensive as that provided by your hosting provider.
- Compatibility: Ensure compatibility between your domain registrar and the chosen third-party nameserver provider before making the switch.
Popular Nameserver Providers
Several reputable nameserver providers offer a range of features and pricing plans.
- Cloudflare: Known for its global network and robust security features, Cloudflare provides a free tier for basic DNS services and paid plans for advanced features like DNSSEC and DDoS protection.
- Google Public DNS: Google’s free public DNS service offers fast and reliable DNS resolution, prioritizing security and privacy.
- Amazon Route 53: Amazon’s cloud-based DNS service offers scalability, high availability, and integration with other AWS services.
- NS1: A leading provider known for its advanced features like traffic management, performance optimization, and comprehensive analytics.
Transferring a Domain to a Different Nameserver Provider
Switching to a third-party nameserver involves updating your domain’s nameserver settings with your domain registrar.
- Obtain Nameserver Information: Get the new nameservers from your chosen third-party provider.
- Access Domain Registrar: Log in to your domain registrar’s control panel.
- Update Nameservers: Navigate to the domain management section and locate the nameserver settings. Replace the existing nameservers with the new ones provided by your third-party provider.
- Confirm Changes: Save the changes and confirm the update. The process can take up to 48 hours for the DNS changes to propagate globally.
Best Practices for Nameserver Management
Managing nameservers effectively is crucial for maintaining a stable and reliable website. By implementing best practices, you can ensure your website is accessible, performant, and secure.
Regular Monitoring and Maintenance
Regular monitoring and maintenance of your nameservers are essential for preventing issues and ensuring optimal performance. This includes checking for errors, updating settings, and monitoring server performance.
- Monitor DNS Records: Regularly check your DNS records for any errors or inconsistencies. Use tools like DNS checkers or your domain registrar’s interface to verify the accuracy of your records.
- Check Server Logs: Review your server logs for any unusual activity or error messages. This can help identify potential problems early on and take corrective actions.
- Update Nameserver Software: Keep your nameserver software up to date with the latest security patches and bug fixes. This minimizes the risk of vulnerabilities and improves overall security.
- Monitor Server Performance: Track your server’s performance metrics, such as CPU usage, memory consumption, and disk space. Identify any bottlenecks or resource constraints that may impact website performance.
Creating Backups of Nameserver Settings
Creating backups of your nameserver settings is essential for disaster recovery. In case of accidental changes or server failures, you can easily restore your settings to their previous state.
- Regularly Export DNS Records: Export your DNS records to a text file or spreadsheet on a regular basis. This allows you to easily restore them if needed.
- Utilize Backup Software: Use specialized backup software designed for nameservers to automate the backup process and ensure data integrity.
- Store Backups Offsite: Store your backups in a secure location, preferably offsite, to prevent data loss in case of server failures or natural disasters.
Closing Notes
Mastering Bluehost nameservers empowers you to take control of your website’s online identity, ensuring its smooth operation and optimal performance. By understanding the role of nameservers, utilizing default settings effectively, customizing them when necessary, and implementing best practices for management, you can confidently navigate the complexities of domain management and enjoy a seamless online experience.