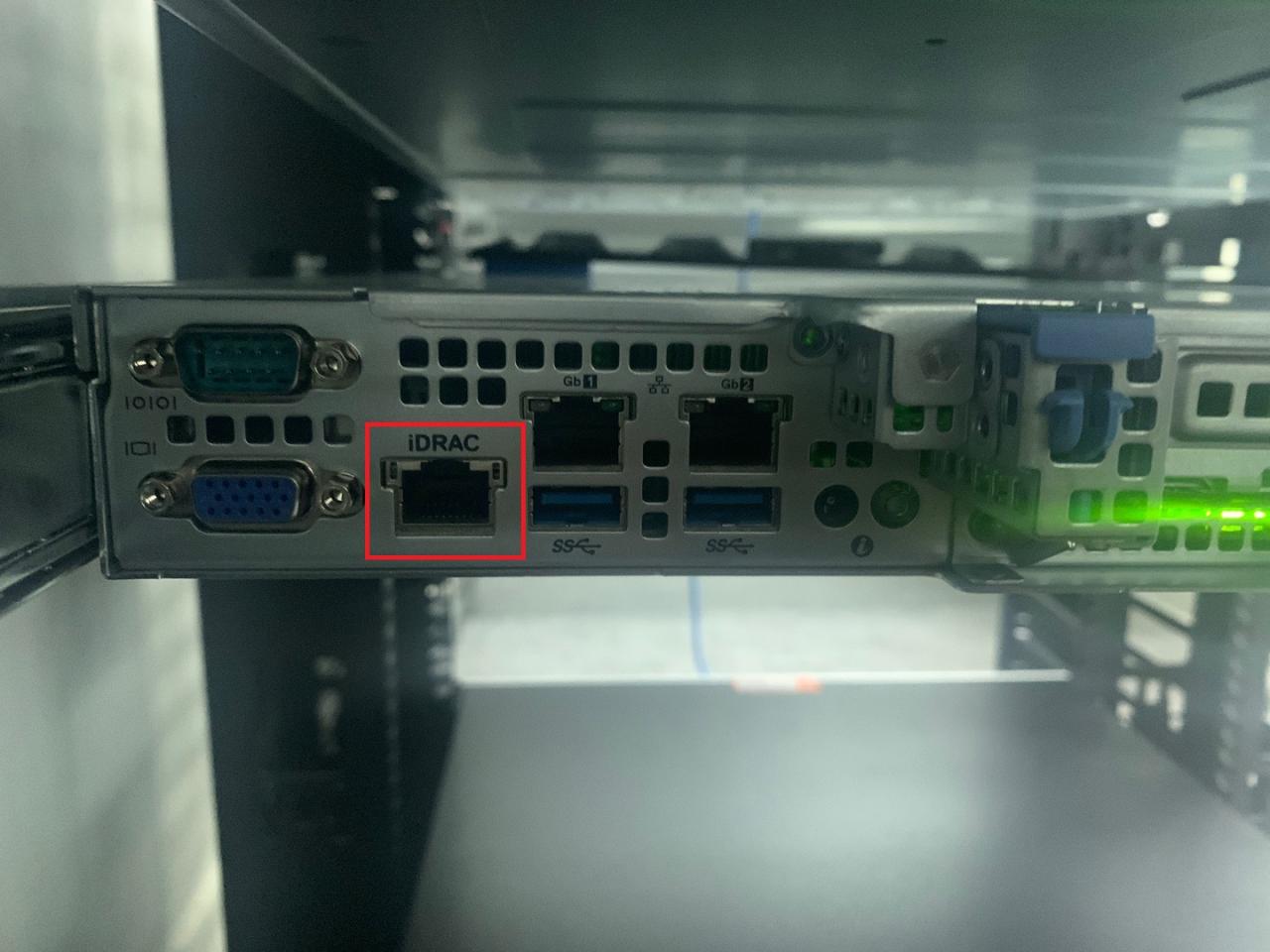
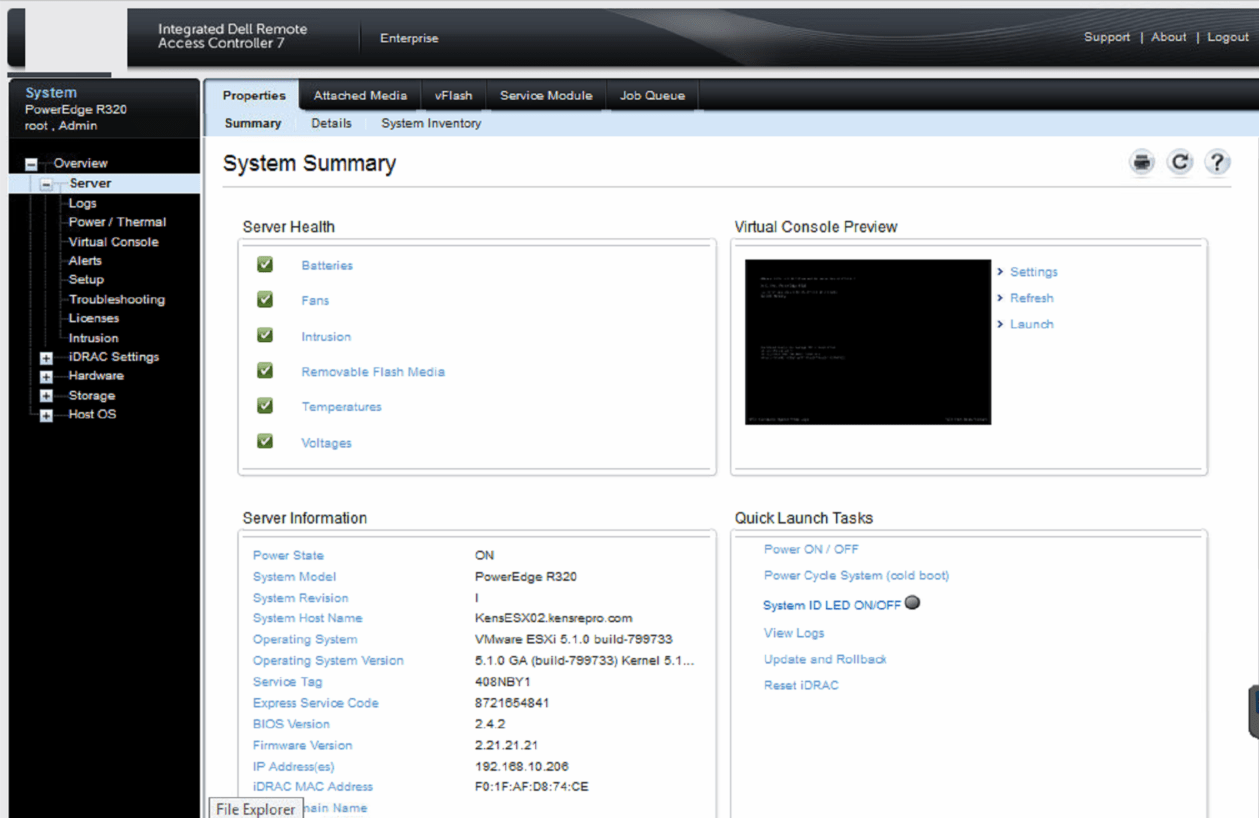
IDRAC Dell is a powerful, built-in management tool found in Dell servers that revolutionizes how IT professionals monitor, troubleshoot, and manage their server infrastructure. It’s essentially a dedicated remote management controller, providing a comprehensive set of features that simplify server administration and empower you to stay on top of your server’s health and performance.
IDRAC empowers you to remotely access and control your servers, enabling you to perform tasks like rebooting, updating firmware, and monitoring system health, all from a single, intuitive interface. This eliminates the need for physical access to the server, saving valuable time and effort while increasing operational efficiency.
IDRAC Dell Overview
IDRAC, short for Integrated Dell Remote Access Controller, is a dedicated hardware component embedded in Dell servers that enables remote management and monitoring. It provides a secure and reliable way to manage and troubleshoot servers, even when they are not accessible through the operating system.
IDRAC Features and Capabilities
IDRAC offers a wide range of features that simplify server management and troubleshooting. Some of the key features include:
- Remote Server Power Management: IDRAC allows administrators to remotely power on, power off, reset, and reboot servers, even if the operating system is not responding.
- Remote Console Access: IDRAC provides a virtual console that allows administrators to access the server’s BIOS, boot menu, and operating system console remotely, providing a direct connection to the server’s hardware and software.
- Server Health Monitoring: IDRAC continuously monitors the server’s health and performance, including temperature, fan speed, voltage, and other critical parameters. It can generate alerts and notifications when issues are detected.
- Firmware Updates: IDRAC allows administrators to update the server’s firmware, including BIOS, drivers, and other components, remotely and securely.
- Virtual Media Support: IDRAC enables administrators to mount virtual media, such as ISO images, to the server remotely, facilitating software installations and operating system deployments.
- Secure Access and Authentication: IDRAC supports secure authentication methods, such as HTTPS and SSH, to protect sensitive data and ensure only authorized personnel can access the server.
Benefits of Using IDRAC
Using IDRAC offers numerous benefits for server administrators and organizations:
- Reduced Downtime: IDRAC enables remote troubleshooting and remediation, minimizing downtime by allowing administrators to resolve issues without physically accessing the server.
- Improved Server Management Efficiency: IDRAC streamlines server management tasks, such as power management, firmware updates, and monitoring, saving time and effort for administrators.
- Enhanced Security: IDRAC’s secure access controls and authentication mechanisms protect the server from unauthorized access and potential security breaches.
- Increased Server Availability: IDRAC’s proactive health monitoring and alerting capabilities help identify and address potential issues before they escalate, ensuring higher server uptime and availability.
- Simplified Disaster Recovery: IDRAC can be used to remotely restore servers from backups, facilitating faster disaster recovery and minimizing business disruption.
IDRAC Monitoring and Diagnostics
IDRAC offers comprehensive monitoring and diagnostic capabilities that provide valuable insights into the health and performance of Dell servers. This feature empowers administrators to proactively identify potential issues, troubleshoot problems, and maintain optimal system uptime.
System Health Monitoring
IDRAC provides real-time monitoring of critical system parameters, including CPU utilization, memory usage, storage space, and network connectivity. This information is presented in a user-friendly interface, allowing administrators to quickly assess the overall health of the server.
- CPU Utilization: IDRAC monitors the CPU usage of the server, displaying the percentage of CPU time used by processes. This helps identify potential bottlenecks and performance issues.
- Memory Usage: IDRAC tracks the amount of RAM used by the server, highlighting potential memory shortages that could impact performance.
- Storage Space: IDRAC monitors the available disk space on the server, providing alerts when storage capacity is nearing its limit.
- Network Connectivity: IDRAC monitors network interfaces, displaying information about network traffic, connectivity status, and potential issues.
Temperature and Fan Speed Monitoring
IDRAC monitors critical hardware components, including the CPU, motherboard, and hard drives, to ensure optimal operating temperatures. It also monitors fan speeds to ensure proper cooling.
- Temperature Monitoring: IDRAC tracks the temperature of key components, providing alerts when temperatures exceed predefined thresholds. This helps prevent overheating and potential hardware damage.
- Fan Speed Monitoring: IDRAC monitors the speed of the server’s fans, ensuring they are operating correctly to maintain adequate cooling.
Troubleshooting Hardware Issues
IDRAC facilitates troubleshooting hardware issues by providing detailed diagnostic information. It allows administrators to perform hardware diagnostics, view error logs, and identify failing components.
- Hardware Diagnostics: IDRAC offers built-in diagnostic tools that can test various hardware components, such as memory, hard drives, and network interfaces. This helps pinpoint faulty components and expedite troubleshooting.
- Error Logs: IDRAC captures system events and errors, providing a detailed log of hardware failures and other issues. These logs are invaluable for identifying the root cause of problems and implementing corrective measures.
Generating Logs and Reports
IDRAC provides the ability to generate logs and reports for further analysis. These logs can be used to identify trends, track performance, and document troubleshooting steps.
- Event Logs: IDRAC captures system events, including hardware failures, software errors, and security events. These logs provide a comprehensive record of system activity, enabling administrators to analyze past events and identify patterns.
- Performance Logs: IDRAC can capture performance metrics, such as CPU utilization, memory usage, and disk I/O. These logs allow administrators to track system performance over time and identify potential bottlenecks or areas for optimization.
- Diagnostic Reports: IDRAC can generate diagnostic reports that provide detailed information about the server’s hardware and software configuration. These reports can be used for troubleshooting, planning, and documentation purposes.
IDRAC Remote Management
IDRAC’s remote management capabilities provide administrators with the ability to manage Dell servers remotely, regardless of physical location. This includes various functionalities like remote power control, virtual media access, and KVM access, enabling administrators to perform essential tasks without being physically present at the server.
Remote Power Control
Remote power control enables administrators to power on, power off, and reset servers remotely. This feature is crucial for managing servers in remote locations or data centers, as it eliminates the need for physical access. The power control functionality can be accessed through the IDRAC web interface, command-line interface (CLI), or third-party management tools.
Virtual Media
IDRAC’s virtual media feature allows administrators to mount ISO images or virtual floppy disk images to servers remotely. This enables administrators to install operating systems, update firmware, or perform other tasks that require access to media files without physically connecting media devices.
KVM Access
KVM access, short for Keyboard, Video, and Mouse, provides administrators with a remote graphical interface to the server’s console. This allows administrators to interact with the server’s operating system, view the console output, and troubleshoot issues remotely.
Managing Multiple Servers Remotely
IDRAC can be used to manage multiple servers remotely through its integrated features. For instance, administrators can use the IDRAC web interface to manage multiple servers simultaneously, performing tasks like power control, firmware updates, and monitoring. This simplifies management and reduces the time and effort required to manage a large number of servers.
Best Practices for Configuring and Securing Remote Management Access
To ensure secure and efficient remote management, it is essential to follow best practices for configuring and securing IDRAC access.
- Enable strong authentication: Use strong passwords and multi-factor authentication (MFA) to protect access to IDRAC. This helps prevent unauthorized access and ensures only authorized personnel can manage the servers.
- Limit access: Only grant access to authorized users and limit access to specific functions based on their roles and responsibilities. This ensures that only individuals with the necessary permissions can access sensitive data and functionalities.
- Use secure protocols: Utilize secure protocols like HTTPS and SSH to encrypt communication between the administrator’s workstation and the IDRAC. This protects data from eavesdropping and unauthorized access.
- Enable logging: Configure IDRAC to log all remote management activities. This helps monitor and audit access to the servers and identify any suspicious activity.
- Keep IDRAC firmware up-to-date: Regularly update the IDRAC firmware to benefit from the latest security patches and bug fixes. This ensures the IDRAC remains secure and functions optimally.
IDRAC Integration with Dell Technologies Software
The iDRAC (Integrated Dell Remote Access Controller) is a powerful management tool that can be integrated with other Dell Technologies software solutions to enhance server management and automation. This integration streamlines server provisioning, deployment, and monitoring, making server management more efficient and effective.
OpenManage Enterprise Integration
OpenManage Enterprise is a comprehensive management platform that allows IT administrators to manage Dell servers, storage, and networking devices from a centralized console. iDRAC integration with OpenManage Enterprise provides a seamless way to manage servers, gather data, and automate tasks.
- Inventory Management: iDRAC provides detailed hardware information to OpenManage Enterprise, allowing administrators to track and manage server inventory efficiently.
- Health Monitoring: iDRAC continuously monitors server health and sends alerts to OpenManage Enterprise, enabling proactive maintenance and problem resolution.
- Remote Management: OpenManage Enterprise leverages iDRAC’s remote management capabilities, allowing administrators to access and manage servers remotely, even from different locations.
- Automated Deployment: iDRAC’s integration with OpenManage Enterprise facilitates automated server provisioning and deployment, streamlining the process and reducing manual intervention.
iDRAC Direct Integration
iDRAC Direct is a feature that allows administrators to manage servers directly through the iDRAC interface, without requiring a separate management console like OpenManage Enterprise.
- Simplified Management: iDRAC Direct simplifies server management by providing a direct interface to the iDRAC, eliminating the need for additional software.
- Quick Access: Administrators can access and manage servers quickly and easily through the iDRAC Direct interface, reducing time and effort.
- Enhanced Security: iDRAC Direct offers secure access to servers, ensuring data confidentiality and integrity.
IDRAC for Virtualization Environments: Idrac Dell
IDRAC plays a crucial role in managing servers within virtualized environments, offering enhanced control and visibility over physical hardware resources. Its integration with leading hypervisors like VMware vSphere and Microsoft Hyper-V streamlines server management, enabling administrators to efficiently monitor, diagnose, and manage virtualized workloads.
Integration with Hypervisors
IDRAC integrates seamlessly with popular hypervisors, providing a unified platform for managing both physical and virtual infrastructure. This integration allows administrators to:
- Discover and manage virtual machines (VMs): IDRAC can discover and manage VMs running on the hypervisor, providing detailed information about their resource utilization, performance metrics, and configuration settings.
- Monitor VM health and performance: IDRAC provides real-time monitoring of VM performance metrics such as CPU usage, memory consumption, and network activity, enabling proactive identification and resolution of performance bottlenecks.
- Control VM power states: Administrators can remotely power on, power off, reset, or suspend VMs directly through IDRAC, simplifying management tasks.
- Configure VM resource allocation: IDRAC allows administrators to adjust the resource allocation for VMs, ensuring optimal performance and resource utilization within the virtualized environment.
Optimizing Server Performance in Virtualized Environments
IDRAC offers several features that optimize server performance in virtualized environments:
- Resource allocation optimization: IDRAC allows administrators to fine-tune resource allocation for VMs, ensuring that each VM receives the necessary resources for optimal performance. For example, administrators can adjust CPU cores, memory, and network bandwidth allocation based on the specific requirements of each VM.
- Performance monitoring and analysis: IDRAC provides comprehensive performance monitoring and analysis tools that help identify and troubleshoot performance bottlenecks. By analyzing performance metrics such as CPU utilization, memory usage, and disk I/O, administrators can identify areas for improvement and optimize server performance.
- Proactive performance management: IDRAC’s proactive performance management features allow administrators to set performance thresholds and receive alerts when specific metrics exceed predefined limits. This enables early detection of performance issues and allows for timely intervention before they impact the virtualized environment.
Examples of IDRAC in Virtualized Environments
- VMware vSphere Integration: IDRAC integrates with VMware vSphere, allowing administrators to manage servers and VMs from a single console. This integration enables centralized management of physical and virtual resources, simplifying infrastructure management and reducing operational overhead.
- Microsoft Hyper-V Integration: IDRAC also integrates with Microsoft Hyper-V, providing similar capabilities for managing servers and VMs in a Hyper-V environment. This integration streamlines server management tasks, offering a unified platform for managing physical and virtual infrastructure.
- Performance Optimization Example: In a virtualized environment with several VMs running on a single server, IDRAC can be used to monitor the resource utilization of each VM. By analyzing performance metrics, administrators can identify VMs that are consuming excessive resources and adjust their resource allocation accordingly. This ensures that all VMs receive the necessary resources for optimal performance and prevents performance bottlenecks caused by resource contention.
IDRAC Security Considerations
IDRAC, while a powerful tool for managing Dell servers, also presents security vulnerabilities that require careful attention. This section explores the security risks associated with IDRAC and provides best practices for mitigating these risks.
Security Vulnerabilities
IDRAC, like any network-accessible management interface, is susceptible to various security vulnerabilities. These vulnerabilities can be exploited by malicious actors to gain unauthorized access to your servers, potentially leading to data breaches, system compromise, or denial of service attacks.
- Default Credentials: Using default credentials for IDRAC access creates a significant security risk. Attackers can easily exploit these default credentials to gain unauthorized access.
- Weak Passwords: Using weak or easily guessable passwords for IDRAC access makes it vulnerable to brute-force attacks, where attackers try various combinations of passwords until they find the correct one.
- Unpatched Software: Outdated IDRAC firmware and software can contain known security vulnerabilities that attackers can exploit. Regularly updating IDRAC to the latest versions is crucial for mitigating these risks.
- Open Ports: Leaving unnecessary ports open on the network can provide attackers with access points to exploit vulnerabilities.
- Misconfigured Firewalls: Firewalls are essential for protecting IDRAC from unauthorized access. Misconfigured firewalls can create loopholes that attackers can exploit.
Configuring IDRAC Security Settings
Properly configuring IDRAC security settings is critical for protecting your servers from unauthorized access. Here are some key security settings to consider:
- Change Default Credentials: Immediately change the default IDRAC username and password to strong, unique credentials.
- Enable Strong Authentication: Implement strong authentication mechanisms like two-factor authentication (2FA) to enhance IDRAC security. This requires users to provide two forms of authentication, such as a password and a one-time code from a mobile device.
- Enable SSL/TLS Encryption: Ensure all communication between IDRAC and management consoles is encrypted using SSL/TLS. This protects data in transit from eavesdropping.
- Restrict Access: Configure IDRAC to only allow access from authorized IP addresses or networks. This prevents unauthorized access from outside your network.
- Enable Audit Logging: Enable IDRAC audit logging to track all access attempts and changes made to the system. This helps in identifying suspicious activity and security breaches.
- Disable Unnecessary Services: Disable any unnecessary services or protocols that are not required for managing your servers. This reduces the attack surface and minimizes potential vulnerabilities.
- Implement Access Control Lists (ACLs): Use ACLs to restrict access to specific resources based on user roles or permissions. This helps in controlling access to sensitive data and configuration settings.
- Keep IDRAC Firmware and Software Up-to-Date: Regularly update IDRAC firmware and software to patch known vulnerabilities and improve security.
Implementing Strong Authentication and Access Control Measures, Idrac dell
Strong authentication and access control are crucial for protecting IDRAC from unauthorized access. Here are some recommendations:
- Two-Factor Authentication (2FA): Implement 2FA for all IDRAC users to add an extra layer of security. This requires users to provide two forms of authentication, such as a password and a one-time code from a mobile device.
- Role-Based Access Control (RBAC): Implement RBAC to assign different levels of access permissions based on user roles. This ensures that users only have access to the resources they need to perform their tasks.
- Password Complexity Requirements: Enforce strong password policies that require users to create complex passwords with a minimum length and a mix of uppercase letters, lowercase letters, numbers, and special characters.
- Password Expiration Policies: Implement password expiration policies to force users to change their passwords regularly. This helps in reducing the risk of compromised passwords being used for extended periods.
- Password Recovery Procedures: Establish secure password recovery procedures that require users to verify their identity before resetting their passwords.
IDRAC Use Cases and Best Practices
IDRAC, Dell’s integrated remote access controller, provides a powerful set of tools for managing and monitoring Dell servers. Understanding its capabilities and implementing best practices can significantly improve server administration efficiency and ensure system uptime. This section will explore real-world IDRAC use cases, best practices for effective utilization, and common challenges encountered during implementation and management.
Real-World IDRAC Use Cases
IDRAC finds applications in diverse IT environments, facilitating various tasks and enhancing overall server management. Here are some real-world examples:
- Remote Server Management: IT administrators can remotely access and manage servers, perform tasks like power cycling, BIOS updates, and software installations, regardless of their physical location. This is particularly valuable for geographically dispersed data centers or servers located in remote or challenging environments.
- Troubleshooting and Diagnostics: IDRAC provides comprehensive diagnostic tools, enabling administrators to identify and resolve hardware and software issues remotely. This includes accessing system logs, running hardware diagnostics, and monitoring real-time performance metrics. This reduces downtime and minimizes the need for on-site visits, saving time and resources.
- Out-of-Band Management: In case of network failures or operating system issues, IDRAC offers out-of-band management capabilities. This allows administrators to access and manage servers even when the primary network is unavailable. This is crucial for maintaining server availability and preventing data loss during network outages.
- Virtualization Environments: IDRAC plays a vital role in managing virtualized environments. It enables remote management of individual physical servers within a virtualized infrastructure, facilitating tasks like server provisioning, resource allocation, and performance monitoring.
Best Practices for IDRAC Utilization
Maximizing the benefits of IDRAC requires implementing best practices to ensure efficient and secure server management.
- Regular Security Updates: IDRAC firmware and software should be regularly updated to patch vulnerabilities and enhance security. This includes implementing strong passwords and enabling two-factor authentication for secure access.
- Network Segmentation: IDRAC should be segregated from the main network to prevent unauthorized access and potential security risks. This can be achieved by configuring a dedicated network segment for IDRAC management.
- Monitoring and Alerting: Set up monitoring tools to track IDRAC activity, identify potential issues, and receive alerts for critical events. This proactive approach helps prevent server downtime and ensures early detection of problems.
- Documentation and Standardization: Maintain comprehensive documentation of IDRAC configurations, access credentials, and management procedures. This ensures consistent management practices and simplifies troubleshooting efforts.
Common IDRAC Challenges and Solutions
Implementing and managing IDRAC can present some challenges, but these can be addressed with appropriate solutions.
- Access Control and Security: Ensuring secure access to IDRAC is crucial. Implementing strong passwords, enabling two-factor authentication, and regularly reviewing access permissions are essential steps to mitigate security risks.
- Network Connectivity Issues: Network connectivity problems can hinder IDRAC functionality. Troubleshooting network configurations, verifying firewall rules, and ensuring proper network segmentation can resolve connectivity issues.
- Compatibility and Driver Issues: Using compatible drivers and ensuring software compatibility with the specific IDRAC version is important. Regularly updating drivers and verifying compatibility with the operating system can prevent potential issues.
- Performance Monitoring and Troubleshooting: Monitoring IDRAC performance and troubleshooting any issues can be challenging. Leveraging performance monitoring tools, analyzing system logs, and seeking support from Dell technical resources can aid in resolving performance-related issues.
IDRAC Future Directions and Trends
IDRAC technology continues to evolve in response to the changing demands of modern IT environments. As data centers become more complex and demanding, the need for robust and feature-rich remote management solutions is paramount. This section will explore some of the emerging trends and future directions for IDRAC technology.
Advancements in Automation and AI
IDRAC will likely incorporate advanced automation and artificial intelligence (AI) capabilities to streamline management tasks and improve efficiency. For example, AI-powered predictive analytics can anticipate potential hardware failures and proactively alert administrators, minimizing downtime and reducing maintenance costs. Additionally, automation can simplify routine tasks such as firmware updates and system configuration, freeing up IT staff to focus on more strategic initiatives.
Enhanced Security Features
As cyber threats become more sophisticated, IDRAC will need to evolve to address these challenges. Expect advancements in security features, such as:
- Multi-factor authentication (MFA) for enhanced access control.
- Advanced encryption algorithms for data protection during transmission and storage.
- Integrated intrusion detection and prevention systems to mitigate malicious activity.
Integration with Cloud-Based Services
IDRAC will increasingly integrate with cloud-based services, enabling seamless management of hybrid and multi-cloud environments. This integration will facilitate tasks such as:
- Remote provisioning and configuration of servers in the cloud.
- Centralized monitoring and management of both on-premises and cloud-based infrastructure.
- Leveraging cloud-based analytics and reporting for enhanced insights into system performance and health.
Support for Emerging Technologies
IDRAC will need to support emerging technologies such as:
- Edge computing, which requires robust remote management capabilities for distributed systems.
- High-performance computing (HPC), which demands advanced monitoring and diagnostics tools for complex workloads.
- Artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning (ML), which require specialized hardware and software configurations that IDRAC must effectively manage.
Focus on User Experience
Future IDRAC interfaces will prioritize user experience, making them more intuitive and user-friendly. This will include:
- Simplified navigation and access to key features.
- Enhanced visualization tools for better understanding system health and performance.
- Mobile-friendly interfaces for managing servers from anywhere.
Final Wrap-Up

With its comprehensive features, IDRAC Dell offers a robust and flexible solution for managing your server environment. From remote access and monitoring to advanced diagnostics and security measures, IDRAC empowers you to take control of your server infrastructure and optimize its performance. By leveraging the capabilities of IDRAC, you can streamline server management tasks, enhance security, and ensure the smooth operation of your critical IT systems.
IDRAC Dell is a powerful tool for managing your server remotely, but sometimes you need a bit of a creative touch to enhance your workspace. For a stylish and functional upgrade, consider checking out the ikea havsta hack – it’s a great way to build a custom server rack using IKEA furniture.
With a well-organized setup, managing your servers through IDRAC Dell becomes even more efficient.